ACEBench : Qui remporte le point de match dans l'utilisation des outils ?
📃 Article · 🏆 Classement (Mise à jour continue)
Anglais | 中文
📚 Contenu
- 1\. Résumé
- 2\. Statistiques du benchmark
- 3\. Classement
- 4\. Configuration
- 5\. Données
- 6\. Inférence
- 6.1\. Script d'inférence
- 6.2\. Exemples d'inférence
- 7\. Évaluation
- Citation
🛠️ Mises à jour [[Retour en haut]](#content)
[2025.10.29]
1 Nous avons corrigé les réponses possibles dans les ensembles de données normal_atom_enum_9, normal_atom_number_17, et normal_atom_list_34.
📘 1\. Résumé [[Retour en haut]](#content)
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated significant potential in decision-making and reasoning, particularly when integrated with various tools to effectively solve complex problems. However, existing benchmarks for evaluating LLMs' tool usage face several limitations: (1) limited evaluation scenarios, often lacking assessments in real multi-turn dialogue contexts; (2) narrow evaluation dimensions, with insufficient detailed assessments of how LLMs use tools; and (3) reliance on LLMs or real API executions for evaluation, which introduces significant overhead. To address these challenges, we introduce ACEBench, a comprehensive benchmark for assessing tool usage in LLMs. ACEBench categorizes data into three primary types based on evaluation methodology: Normal, Special, and Agent. "Normal" evaluates tool usage in basic scenarios; "Special" evaluates tool usage in situations with ambiguous or incomplete instructions; "Agent" evaluates tool usage through multi-agent interactions to simulate real-world, multi-turn dialogues. We conducted extensive experiments using ACEBench, analyzing various LLMs in-depth and providing a more granular examination of error causes across different data types.
📊 2. Analyse des données de référence [[Retour en haut]](#content)
Domaine des API
- ACEBench couvre 8 grands domaines et 68 sous-domaines, incluant technologie, finance, divertissement, société, santé, culture, environnement, et plus encore.
- Il comprend un total de 4 538 API en chinois et en anglais.
- La répartition des API par domaine est visualisée dans la figure ci-dessous :
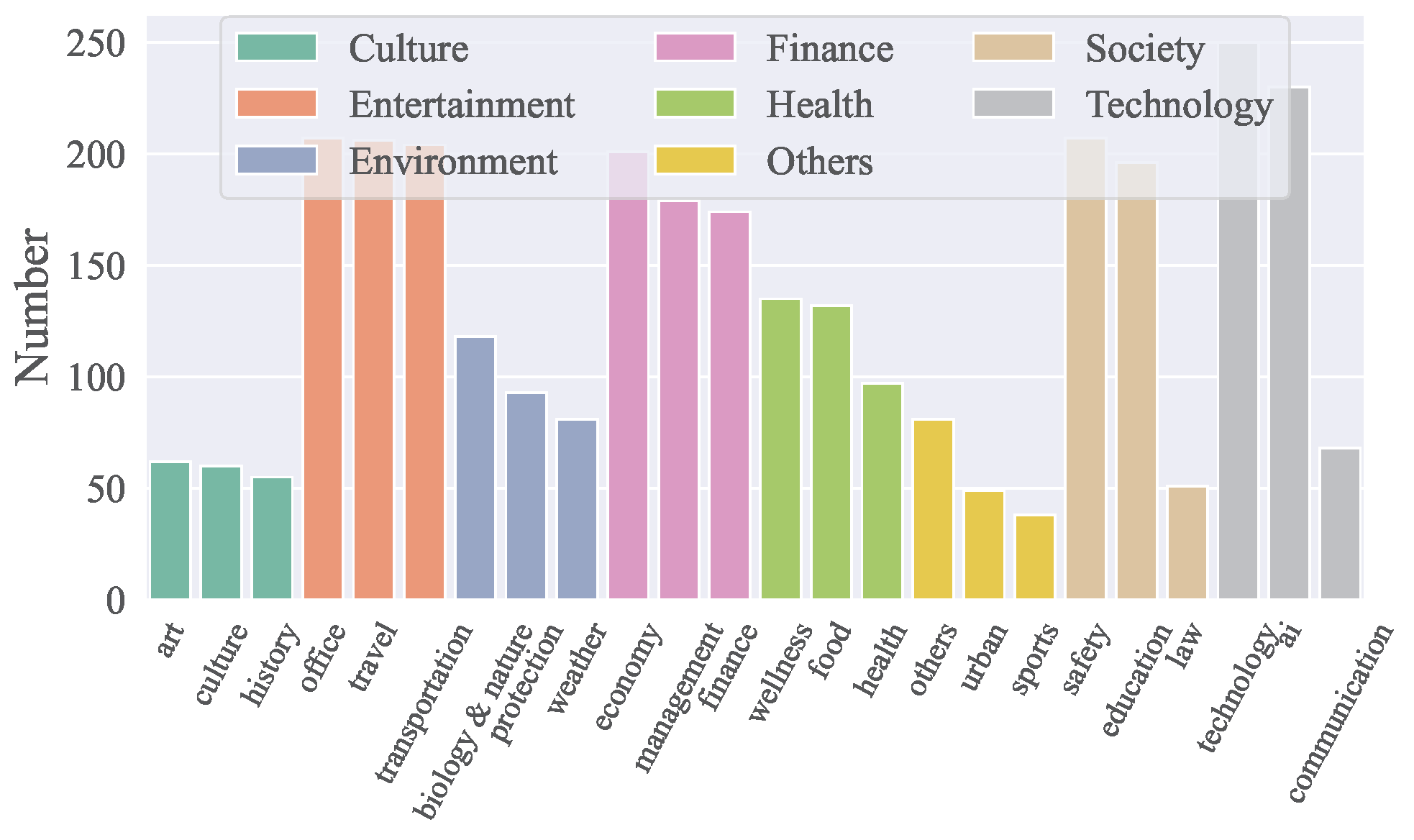
Composition des données
- ACEBench se compose de trois principales catégories d’échantillons de test :
- Normal : scénarios d’utilisation d’outils basiques.
- Agent : interactions multi-tours impliquant utilisateurs et environnements.
- Spécial : scénarios complexes nécessitant plusieurs étapes ou la gestion d’appels d’outils irréalisables.
- La composition des données est visualisée ci-dessous, montrant la couverture complète des capacités d’utilisation d’outils :
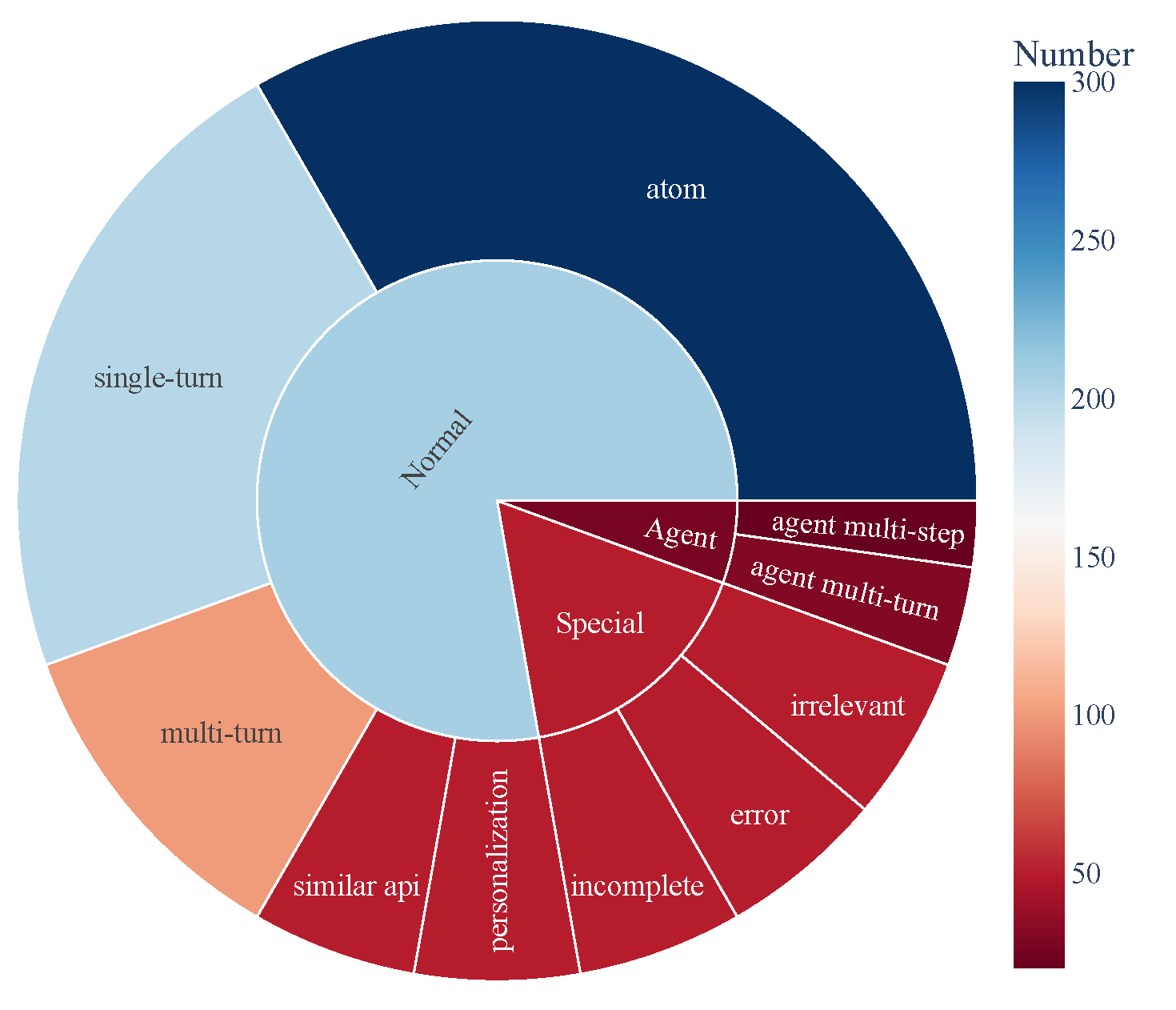
🏆 3\. Classement [[Retour en haut]](#content)
| Modèle | normal | spécial | agent | global | | ------------------------------------- | ------ | ------- | ----- | ------- | | modèle propriétaire | | gpt-4o-2024-11-20 | 0.927 | 0.933 | 0.715 | 0.896 | | gpt-4-turbo-2024-04-09 | 0.917 | 0.913 | 0.725 | 0.886 | | qwen-max | 0.887 | 0.740 | 0.685 | 0.817 | | o1-preview | 0.830 | 0.793 | 0.735 | 0.806 | | deepseek-chat | 0.926 | 0.733 | 0.350 | 0.785 | | gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18 | 0.834 | 0.813 | 0.390 | 0.760 | | claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022 | 0.835 | 0.820 | 0.350 | 0.756 | | gemini-1.5-pro | 0.822 | 0.800 | 0.250 | 0.728 | | o1-mini | 0.774 | 0.673 | 0.610 | 0.722 | | doubao-pro-32k | 0.750 | 0.593 | 0.235 | 0.628 | | modèle open-source | | Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct-local | 0.908 | 0.813 | 0.715 | 0.853 | | Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct-local | 0.852 | 0.747 | 0.690 | 0.799 | | Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct-local | 0.873 | 0.773 | 0.525 | 0.793 | | Qwen2.5-Coder-14B-Instruct-local | 0.868 | 0.647 | 0.525 | 0.756 | | Qwen2.5-14B-Instruct-local | 0.790 | 0.540 | 0.250 | 0.640 | | Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct-local | 0.753 | 0.473 | 0.435 | 0.629 | | Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct-local | 0.759 | 0.447 | 0.125 | 0.578 | | DeepSeek-Coder-V2-Lite-Instruct-local | 0.688 | 0.413 | 0.015 | 0.511 | | Qwen2.5-Coder-7B-Instruct-local | 0.735 | 0.193 | 0.125 | 0.496 | | watt-tool-8B-local | 0.763 | 0.100 | 0.040 | 0.474 | | ToolACE-8B-local | 0.782 | 0.013 | 0.040 | 0.462 | | Hammer2.1-7b-local | 0.627 | 0.260 | 0.185 | 0.461 | | Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-local | 0.450 | 0.267 | 0.040 | 0.338 | | Qwen2.5-Coder-3B-Instruct-local | 0.495 | 0.100 | 0.065 | 0.323 | | Phi-3-mini-128k-instruct-local | 0.389 | 0.253 | 0.015 | 0.295 | | Qwen2.5-3B-Instruct-local | 0.408 | 0.127 | 0.065 | 0.280 | | Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct-local | 0.327 | 0.100 | 0.000 | 0.216 | | xLAM-7b-r-local | 0.187 | 0.013 | 0.075 | 0.123 | | Hammer2.1-3b-local | 0.118 | 0.013 | 0.015 | 0.074 |
🛠️ 4\. Configuration [[Retour en haut]](#content)
Exécutez la commande suivante pour installer les dépendances requises pour l'inférence et l'évaluation :
pip install -r requirements.txt🗂️ 5\. Données [[Retour en haut]](#content)
Toutes les données sont stockées dans le répertoire data_all, divisées en parties anglaise et chinoise, situées respectivement dans les dossiers data_en et data_zh. Chaque dossier contient plusieurs fichiers JSON, nommés au format data_{category}.json, où category représente le type de données.
data_all/
├── possible_answer_en/
│ ├── data_{normal}.json
│ ├── data_{special}.json
│ ├── data_{agent}.json
├── possible_answer_zh/
│ ├── data_{normal}.json
│ ├── data_{special}.json
│ ├── data_{agent}.json
...🧠 6\. Inférence [[Retour en haut]](#content)
6.1 Script d'inférence
Pour exécuter une inférence avec cmodels, utilisez le script generate.py. Ce script prend en charge divers modèles, catégories et langues.
Utilisation de base
python generate.py --model --model_path
--category --language Arguments :
--model: Spécifie le modèle à utiliser pour l'inférence.--model_path: Spécifie le chemin local vers le modèle (uniquement pour les modèles open-source).--category: Définit la catégorie des tâches ou des ensembles de données à évaluer. Les catégories disponibles se trouvent dans eval_checker/eval_checker_constant.py.--language: Spécifie la langue de l'entrée/sortie. Langues supportées : "en" (anglais), "zh" (chinois)
6.2\. Exemples d'inférence
pour modèle propriétaire (closed-source)
python generate.py --model qwen-max --category test_all --language zhpython generate.py --model Qwen2.5-3B-Instruct-local --model-path /mnt/nas/ckpt/Qwen2.5-3B-Instruct --category test_all --language zh6.3\. Précautions
- Avant d'exécuter le programme, assurez-vous que le fichier de variables d'environnement .env est correctement configuré. Pour invoquer OpenAI, vous devez utiliser le réseau externe. Configurez les variables d'environnement https_proxy et http_proxy. Pour utiliser le modèle gemini, vous devez utiliser le proxy japonais.
- Le modèle à évaluer doit être mappé dans model_inference/inference_map.py. Le modèle invoqué via OpenAI peut être ajouté à la liste APIModelInference, et le modèle d'inférence personnalisé peut être ajouté à la liste CommonInference. Le nom d'un modèle local se termine par -local.
- Pour ajouter un modèle d'évaluation personnalisé, ajoutez la classe du modèle à model_dict en vous référant à model_inference/model_infer.py.
- Évaluez le modèle open-source sur Hugging Face. Il est conseillé d'utiliser LLaMA-Factory pour combiner les poids LoRA puis inférer.
📈 7. Évaluation [[Retour en haut]](#content)
Pour évaluer les performances des modèles, utilisez le script eval_main.py. Ce script supporte diverses métriques d'évaluation et peut être utilisé pour les modèles open-source comme fermés.
Utilisation de base
python eval_main.py --model --category --language 📄 Citation
Si vous trouvez notre article et nos ressources utiles, veuillez envisager de citer notre article :
@article{chen2025acebench,
title={ACEBench: Who Wins the Match Point in Tool Learning?},
author={Chen, Chen and Hao, Xinlong and Liu, Weiwen and Huang, Xu and Zeng, Xingshan and Yu, Shuai and Li, Dexun and Wang, Shuai and Gan, Weinan and Huang, Yuefeng and others},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2501.12851},
year={2025}
}--- Tranlated By Open Ai Tx | Last indexed: 2025-12-19 ---